Are you looking to install a solar power system into your home but don’t know where to start? We’ve put together some information on things to consider and how to get started.
What am I actually installing?
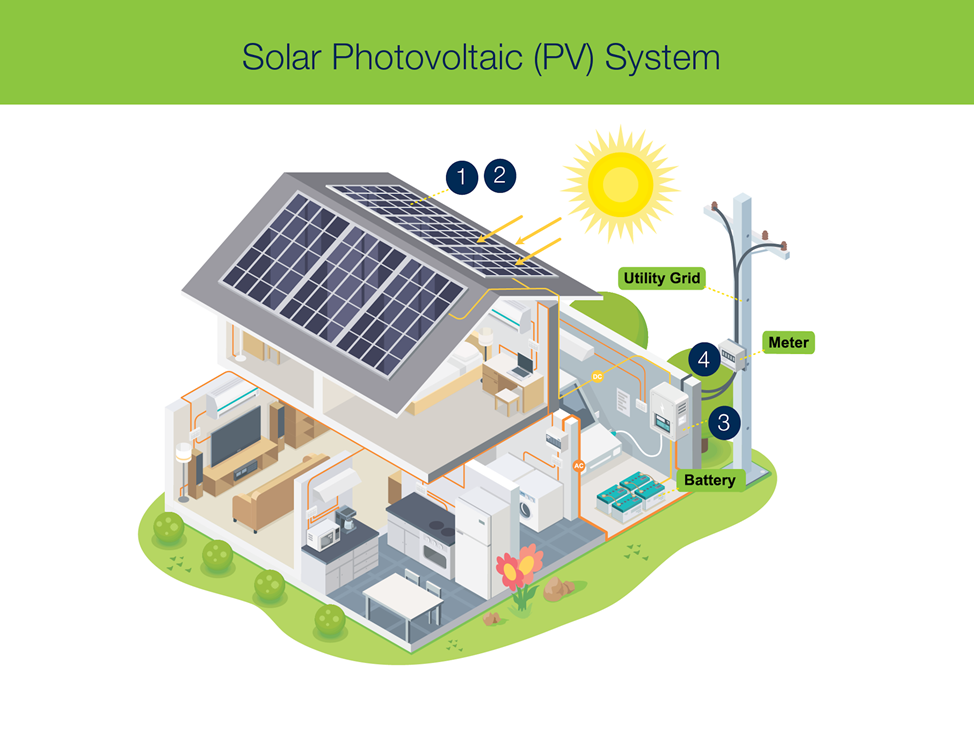
Solar energy is the suns power which is light and heat. Solar photovoltaic (PV) systems collect the sun's energy and convert it into electricity.
There are 4 main components to a PV system:
1. the solar panel/s,
2. mounting
3. an inverter and,
4. utility grid connection.
Solar panels
There are 4 main types of solar panels, outlined below. Discuss which options are best for you with your solar installation professionals.
Monocrystalline solar panels |
Polycrystalline solar panels |
Passivated Emitter and Rear Cell (PERC) panels |
Thin-film solar panels |
|
|
|
|
Mounting
Solar panels can be mounted onto your roof or other parts of your home e.g. outside wall. Mounting to your roof will require a frame and there are several mounting options for frames:
Fixed mount |
Tracking mount |
Adjustable mount |
| The frame is placed at the best position to capture sunlight. This is typically the most inexpensive option. | This can be a more expensive option but may be more energy efficient as the frame moves automatically to track sunlight. | The frame can be adjusted to your needs. |
Your solar provider will be able to highlight the pros and cons of these options depending on your property and the panel type you plan to install.
Inverter
The inverter converts the suns energy collected in solar cells to electricity that can be used at home. The inverter can also feed any excess electricity back into the grid via the utility grid connection.
Utility grid connection
This is needed for supplementary supply for those times when your solar panels don’t produce enough electricity.
Determining how a PV system can meet your energy needs
Before you install a PV system you will need to figure out how many solar panels you need to install. Take the time to understand how your energy needs will be met at night or on overcast days along with what can happen with excess electricity created by your PV system.
How many solar panels do I need to install?
The number and size of panels you need to install will depend on how much energy your household consumes. An easy way to do this is by looking at the average daily use (kWh) on your electricity bill.
Consider future proofing your energy needs, is it likely your household energy use will increase or decrease over time? Things like planning for a family or having adult children move out may impact your energy consumption. Discuss this with your solar provider to ensure you install an appropriate system for your current and future needs.
What happens at night?
You will need to connect to the grid (street powerlines) for your night time electricity needs. You may want to consider adding a battery storage solution to your solar system so it can store excess electricity generated during the day for use at night.
What happens if it's cloudy or rains?
If there is not enough sun power to generate electricity with the PV system you will need to use electricity from the grid. This may also be a consideration for a battery storage solution. We recommend discussing this with your solar provider when scoping your project.
Feed-in tariffs
Excess electricity produced from your solar panels and not used in your home can be returned to the grid. If you are paid for this, it is known as a feed-in tariff. Feed in tariffs can vary from retailer and state so check with your electricity retailer to see if returning solar energy into the gird means you can qualify for a feed in tariff.
What do I need to do to install a solar panel system onto my house?
Below are some considerations for installing solar panels onto your home. Please note, this information is general and is a guide only. It is important you research what is right for your needs and seek the advice of solar professionals.
Seek relevant approvals
Start by checking with your local council to see if you require planning permission to install a solar panel system onto your home. You may need to submit a building application plan which may attract a fee. Also check with your current electricity provider to confirm what you need to do with connecting the inverter to the grid.
Consult the correct trades people
The installation process requires building and electrical work. A licensed electrician should be used for all electrical work.
The Clean Energy Council has an accreditation program for solar and solar battery installers. Use their search tool to find an accredited installer close to you. You can also search your electrician/installer to see if they are accredited.
Insurance
Check your home insurance policy to see if it covers damage to your solar panels as they can get damaged in bad weather conditions.
Maintenance
Ask your solar panel provider about how to clean and maintain the solar panels and other elements of the system to ensure they are in a good condition to operate at optimum capacity.
Government rebates
There are often a range of government benefits or rebates to support consumers wanting to adopt solar or other energy efficiency solutions, these are often specific to your location. Before you install solar it can be helpful to research any benefits or rebates you may be eligible for and can start by searching the Federal Governments Rebates and Assistance page.
The option to qualify for a Gateway Green Home Loan
Gateway rewards customers who make energy efficient enhancements to their home. Alongside the usual credit criteria, if you install a PV system onto your home, along with 2 other environmental features from the list below, you are eligible for a Gateway Green Home Loan which is offered with at least a 0.15% discount from Gateway’s Premium Package Rate (LVR up to 80%) Home Loan.
- Solar photovoltaic (PV) systems / Solar Panels
- Solar battery storage system
- Rain / Storm Water Tank
- Certified double glazed windows
- Solar hot water system
- 5 Star + Gas or Electric Heating
- External awnings
- Solar pool heating system
- Home insulation that meets government standards for geographic area
- Energy efficient LED lights in over 75% of the property
- Split systems, evaporative cooler or star rated zoned air conditioning units with either a minimum energy rating 4/6 stars or minimum 6/10 stars
- Gas Hot Water System
Useful information
Below are links to some useful solar information specific to each Australian state and territory.
New South Wales
Western Australia
South Australia
Tasmania
Victoria
Northern Territory
Australian Renewable Energy Agency
ACT
Queensland





